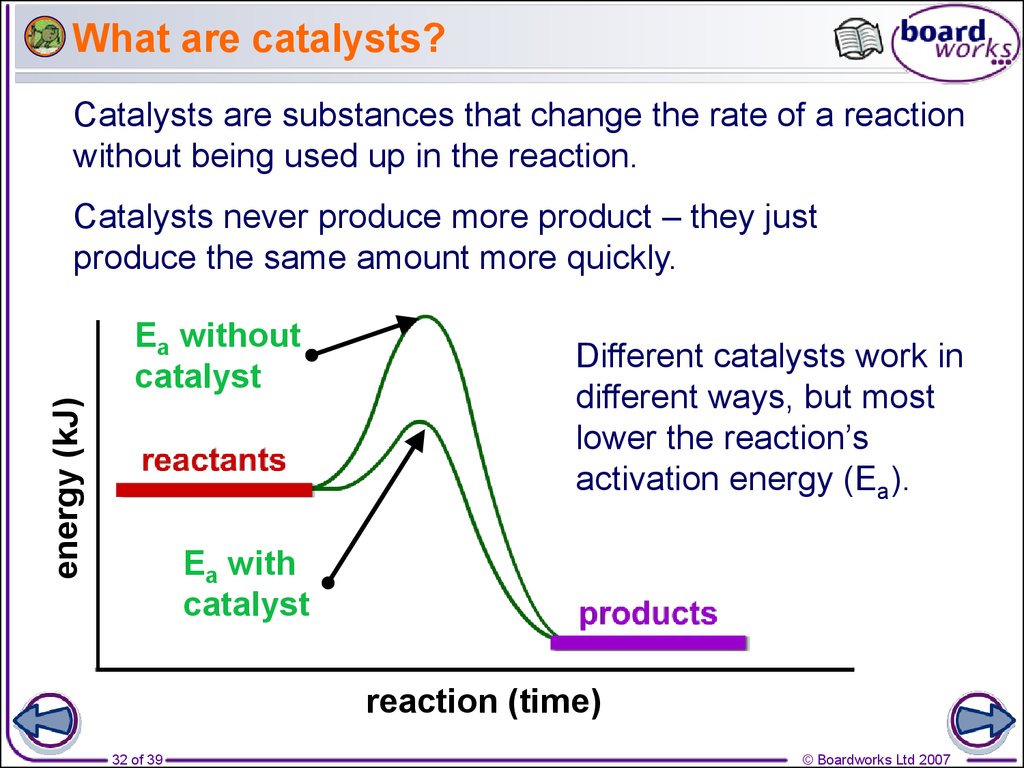
Catalyst Definition In Biology . An entity (organic, inorganic, organometallic, protein or rna) that increases the rate of a reaction without itself. In other words, the catalyst ends up after a reaction just the way it started so it can. Every chemistry student has been taught that a catalyst speeds a reaction without being consumed by it. A fundamental task of proteins is to act as enzymes—catalysts that increase the rate of virtually all the chemical reactions within cells. A catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without being consumed in the process. Enzymes are substances found in biological systems that are catalysts for. Catalyst, in chemistry, any substance that increases the rate of a reaction without itself being consumed. A substance that helps a chemical reaction to occur is a catalyst, and the special. Explain how enzymes function as molecular catalysts. Although rnas are capable of catalyzing some reactions,. Discuss enzyme regulation by various factors.
from ppt-online.org
A substance that helps a chemical reaction to occur is a catalyst, and the special. A catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without being consumed in the process. Enzymes are substances found in biological systems that are catalysts for. Every chemistry student has been taught that a catalyst speeds a reaction without being consumed by it. Explain how enzymes function as molecular catalysts. Catalyst, in chemistry, any substance that increases the rate of a reaction without itself being consumed. An entity (organic, inorganic, organometallic, protein or rna) that increases the rate of a reaction without itself. Discuss enzyme regulation by various factors. A fundamental task of proteins is to act as enzymes—catalysts that increase the rate of virtually all the chemical reactions within cells. Although rnas are capable of catalyzing some reactions,.
Rates of reaction презентация онлайн
Catalyst Definition In Biology Catalyst, in chemistry, any substance that increases the rate of a reaction without itself being consumed. Every chemistry student has been taught that a catalyst speeds a reaction without being consumed by it. Catalyst, in chemistry, any substance that increases the rate of a reaction without itself being consumed. Explain how enzymes function as molecular catalysts. In other words, the catalyst ends up after a reaction just the way it started so it can. A catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without being consumed in the process. A substance that helps a chemical reaction to occur is a catalyst, and the special. An entity (organic, inorganic, organometallic, protein or rna) that increases the rate of a reaction without itself. Enzymes are substances found in biological systems that are catalysts for. A fundamental task of proteins is to act as enzymes—catalysts that increase the rate of virtually all the chemical reactions within cells. Discuss enzyme regulation by various factors. Although rnas are capable of catalyzing some reactions,.
From fity.club
Enzyme The Catalyst Catalyst Definition In Biology Although rnas are capable of catalyzing some reactions,. An entity (organic, inorganic, organometallic, protein or rna) that increases the rate of a reaction without itself. Discuss enzyme regulation by various factors. A fundamental task of proteins is to act as enzymes—catalysts that increase the rate of virtually all the chemical reactions within cells. Explain how enzymes function as molecular catalysts.. Catalyst Definition In Biology.
From bio.libretexts.org
4.1 Basic Principles of Catalysis Biology LibreTexts Catalyst Definition In Biology Every chemistry student has been taught that a catalyst speeds a reaction without being consumed by it. A fundamental task of proteins is to act as enzymes—catalysts that increase the rate of virtually all the chemical reactions within cells. Catalyst, in chemistry, any substance that increases the rate of a reaction without itself being consumed. In other words, the catalyst. Catalyst Definition In Biology.
From www.worksheetsplanet.com
What is a Catalyst Definition of Catalyst Catalyst Definition In Biology Enzymes are substances found in biological systems that are catalysts for. An entity (organic, inorganic, organometallic, protein or rna) that increases the rate of a reaction without itself. Although rnas are capable of catalyzing some reactions,. In other words, the catalyst ends up after a reaction just the way it started so it can. Every chemistry student has been taught. Catalyst Definition In Biology.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT CATALYSIS AND CATALYTIC REACTION MECHANISM PART 1 PowerPoint Catalyst Definition In Biology Discuss enzyme regulation by various factors. A substance that helps a chemical reaction to occur is a catalyst, and the special. An entity (organic, inorganic, organometallic, protein or rna) that increases the rate of a reaction without itself. Explain how enzymes function as molecular catalysts. Every chemistry student has been taught that a catalyst speeds a reaction without being consumed. Catalyst Definition In Biology.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Starter 1)Definition of catalysts 2) Difference between Catalyst Definition In Biology In other words, the catalyst ends up after a reaction just the way it started so it can. A substance that helps a chemical reaction to occur is a catalyst, and the special. An entity (organic, inorganic, organometallic, protein or rna) that increases the rate of a reaction without itself. Enzymes are substances found in biological systems that are catalysts. Catalyst Definition In Biology.
From www.meritnation.com
Illustrate graphically the effect of a catalyst on rate of a reaction Catalyst Definition In Biology In other words, the catalyst ends up after a reaction just the way it started so it can. Enzymes are substances found in biological systems that are catalysts for. Discuss enzyme regulation by various factors. An entity (organic, inorganic, organometallic, protein or rna) that increases the rate of a reaction without itself. A fundamental task of proteins is to act. Catalyst Definition In Biology.
From ar.inspiredpencil.com
Catalyst Examples For Kids Catalyst Definition In Biology A fundamental task of proteins is to act as enzymes—catalysts that increase the rate of virtually all the chemical reactions within cells. Explain how enzymes function as molecular catalysts. An entity (organic, inorganic, organometallic, protein or rna) that increases the rate of a reaction without itself. In other words, the catalyst ends up after a reaction just the way it. Catalyst Definition In Biology.
From study.com
Catalyst Definition, Types & Function Lesson Catalyst Definition In Biology Every chemistry student has been taught that a catalyst speeds a reaction without being consumed by it. A catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without being consumed in the process. Catalyst, in chemistry, any substance that increases the rate of a reaction without itself being consumed. In other words, the catalyst ends up after. Catalyst Definition In Biology.
From ppt-online.org
Rates of reaction презентация онлайн Catalyst Definition In Biology Catalyst, in chemistry, any substance that increases the rate of a reaction without itself being consumed. Although rnas are capable of catalyzing some reactions,. A substance that helps a chemical reaction to occur is a catalyst, and the special. An entity (organic, inorganic, organometallic, protein or rna) that increases the rate of a reaction without itself. Discuss enzyme regulation by. Catalyst Definition In Biology.
From www.dreamstime.com
Catalyst Surface with Catalytic Reaction Stock Vector Illustration of Catalyst Definition In Biology Every chemistry student has been taught that a catalyst speeds a reaction without being consumed by it. Catalyst, in chemistry, any substance that increases the rate of a reaction without itself being consumed. Explain how enzymes function as molecular catalysts. Enzymes are substances found in biological systems that are catalysts for. A fundamental task of proteins is to act as. Catalyst Definition In Biology.
From www.thoughtco.com
Catalysis Definition in Chemistry Catalyst Definition In Biology Catalyst, in chemistry, any substance that increases the rate of a reaction without itself being consumed. Explain how enzymes function as molecular catalysts. Enzymes are substances found in biological systems that are catalysts for. Although rnas are capable of catalyzing some reactions,. An entity (organic, inorganic, organometallic, protein or rna) that increases the rate of a reaction without itself. A. Catalyst Definition In Biology.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Enzymes as Biological Catalysts PowerPoint Presentation ID591293 Catalyst Definition In Biology Catalyst, in chemistry, any substance that increases the rate of a reaction without itself being consumed. A catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without being consumed in the process. A fundamental task of proteins is to act as enzymes—catalysts that increase the rate of virtually all the chemical reactions within cells. Although rnas are. Catalyst Definition In Biology.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT 23.5 Features of homogeneous catalysis PowerPoint Presentation Catalyst Definition In Biology Although rnas are capable of catalyzing some reactions,. An entity (organic, inorganic, organometallic, protein or rna) that increases the rate of a reaction without itself. A catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without being consumed in the process. A substance that helps a chemical reaction to occur is a catalyst, and the special. Every. Catalyst Definition In Biology.
From www.youtube.com
Enzyme Catalysis How Do Enzymes Work? AP Biology 3.2 YouTube Catalyst Definition In Biology A catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without being consumed in the process. Every chemistry student has been taught that a catalyst speeds a reaction without being consumed by it. In other words, the catalyst ends up after a reaction just the way it started so it can. A substance that helps a chemical. Catalyst Definition In Biology.
From www.nagwa.com
Question Video Defining an Enzyme as a Catalyst Nagwa Catalyst Definition In Biology In other words, the catalyst ends up after a reaction just the way it started so it can. Enzymes are substances found in biological systems that are catalysts for. Although rnas are capable of catalyzing some reactions,. Catalyst, in chemistry, any substance that increases the rate of a reaction without itself being consumed. Discuss enzyme regulation by various factors. Explain. Catalyst Definition In Biology.
From www.pinterest.com
Catalyst Easy Science Energy activities, Chemical reactions Catalyst Definition In Biology In other words, the catalyst ends up after a reaction just the way it started so it can. An entity (organic, inorganic, organometallic, protein or rna) that increases the rate of a reaction without itself. A catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without being consumed in the process. Catalyst, in chemistry, any substance that. Catalyst Definition In Biology.
From www.thoughtco.com
Catalysts and How They Work Catalyst Definition In Biology An entity (organic, inorganic, organometallic, protein or rna) that increases the rate of a reaction without itself. Explain how enzymes function as molecular catalysts. A catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without being consumed in the process. Every chemistry student has been taught that a catalyst speeds a reaction without being consumed by it.. Catalyst Definition In Biology.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Enzymes Biological Catalysts PowerPoint Presentation ID5736986 Catalyst Definition In Biology Catalyst, in chemistry, any substance that increases the rate of a reaction without itself being consumed. An entity (organic, inorganic, organometallic, protein or rna) that increases the rate of a reaction without itself. In other words, the catalyst ends up after a reaction just the way it started so it can. A catalyst is a substance that increases the rate. Catalyst Definition In Biology.